在启动过程中,bootstrap模块里在创建完injector注入器之后,便开始编译整个文档了,源码如下:
injector.invoke(['$rootScope', '$rootElement', '$compile', '$injector', '$animate',
function(scope, element, compile, injector, animate) {
scope.$apply(function() {
element.data('$injector', injector);
compile(element)(scope);
});
}
]);
其中,主要的代码是下面一行
compile(element)(scope);
这是两个过程,分别是
- compile(element):在初始化之后,从
$rootElement开始编译,递归地收集所有的指令,将连接函数publicLinkFn以闭包的形式返回。 - publicLinkFn(scope):传入
$rootScope参数,进行链接过程,完成整个页面的链接和scope分绑定。
整个编译链接过程,如下图所示:
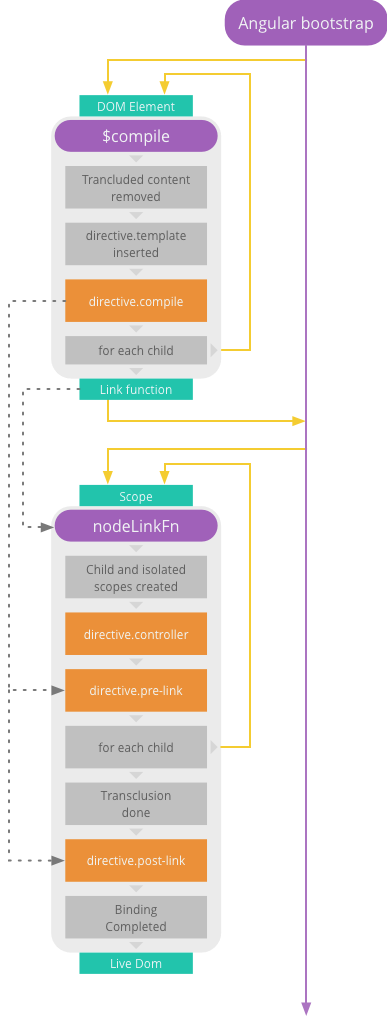
预处理
在编译过程中引用$compile是在publishExternalAPI中完成的,将所有的内置指令都添加到$CompileProvider中进行注册,添加到hasDirective对象中,后面在查找指令时进行匹配。
源码如下:
$provide.provider('$compile', $CompileProvider).
directive({
a: htmlAnchorDirective,
input: inputDirective,
textarea: inputDirective,
form: formDirective,
script: scriptDirective,
select: selectDirective,
style: styleDirective,
//省略若干行
}).
directive({
ngInclude: ngIncludeFillContentDirective
}).
directive(ngAttributeAliasDirectives).
directive(ngEventDirectives);
compile(element)
compile方法负责进行指令的收集和编译,其中流程如下:
- 当当前节点为文本节点时,进行
<span>包装。 - 利用
compileNodes编译当前的节点,并返回连接函数到compositeLinkFn。 - 调用
compile.$$addScopeClass创建scope class. - 返回一个publicLinkFn的闭包,即后面执行的链接函数。
源码如下:
function compile($compileNodes, transcludeFn, maxPriority, ignoreDirective, previousCompileContext) {
// 对于文本节点,使用<span>包装
forEach($compileNodes, function(node, index) {
if (node.nodeType == NODE_TYPE_TEXT && node.nodeValue.match(/\S+/)) {
$compileNodes[index] = jqLite(node).wrap('<span></span>').parent()[0];
}
});
// 调用compileNodes编译当前节点,返回链接函数
var compositeLinkFn =
compileNodes($compileNodes, transcludeFn, $compileNodes, maxPriority, ignoreDirective, previousCompileContext);
// 添加scope class
compile.$$addScopeClass($compileNodes);
var namespace = null;
return function publicLinkFn(scope, cloneConnectFn, options) {
// 后面再看
};
}
compileNodes
在compileNodes中,首先对传入的节点进行遍历,具体过程如下:
- 调用
collectDirectives收集每个节点的指令,存到directives数组中。 - 若某个节点中含有指令,则利用
applyDirectivesToNode将指令应用到该节点,这两个函数后面详细分析。 - 如果某个节点存在链接函数,则向该节点绑定
ng-scope的class。 - 递归遍历该节点的子节点,获得连接函数存入
childLinkFn。 - 将nodeLinkFn和childLinkFn存入linkFns数组中,在最后的链接过程中使用,并返回闭包函数
compositeLinkFn。
源码如下:
function compileNodes(nodeList, transcludeFn, $rootElement, maxPriority, ignoreDirective, previousCompileContext) {
var linkFns = [],
attrs, directives, nodeLinkFn, childNodes, childLinkFn, linkFnFound, nodeLinkFnFound;
// 遍历当前层的所有节点
for (var i = 0; i < nodeList.length; i++) {
attrs = new Attributes();
// 收集每个节点上的所有指令
directives = collectDirectives(nodeList[i], [], attrs, i === 0 ? maxPriority : undefined, ignoreDirective);
// 应用指令,返回链接函数
nodeLinkFn = (directives.length)
? applyDirectivesToNode(directives, nodeList[i], attrs, transcludeFn, $rootElement, null, [], [], previousCompileContext)
: null;
// 添加scope class
if (nodeLinkFn && nodeLinkFn.scope) {
compile.$$addScopeClass(attrs.$$element);
}
// 如果父亲节点没有链接函数或者已终止(terminal)
// 或者没有孩子节点
// 孩子节点的链接函数就为null
// 否则递归编译孩子节点
childLinkFn = (nodeLinkFn && nodeLinkFn.terminal ||
!(childNodes = nodeList[i].childNodes) ||
!childNodes.length)
? null
: compileNodes(childNodes,
nodeLinkFn ? (
(nodeLinkFn.transcludeOnThisElement || !nodeLinkFn.templateOnThisElement)
&& nodeLinkFn.transclude) : transcludeFn);
// 将当前节点的链接函数和孩子节点的链接函数都插入到linkFns数组中
if (nodeLinkFn || childLinkFn) {
linkFns.push(i, nodeLinkFn, childLinkFn);
linkFnFound = true;
nodeLinkFnFound = nodeLinkFnFound || nodeLinkFn;
}
previousCompileContext = null;
}
// 如果有链接函数返回闭包(compositeLinkFn能访问linkFns)
return linkFnFound ? compositeLinkFn : null;
function compositeLinkFn(scope, nodeList, $rootElement, parentBoundTranscludeFn) {
// 代码略,后面再说
}
}
collectDirectives
当收集某个节点的指令时,有三种类型:
- element node:当为元素节点时,首先根据
tagName调用addDirective来添加指令,遍历该节点的attrs调用addAttrInterpolateDirective和addDirective来添加指令,通过className调用addDirective来添加指令。 - text node:当为文本节点时,调用
addTextInterpolateDirective来添加指令。 - comment node:当该节点为注释时,调用
addDirective来添加指令。
其中涉及addDirective、addAttrInterpolateDirective和addTextInterpolateDirective三个方法,下面依次分析一下:
addDirective
如果hasDirectives中存在当前指令,则获取该指令的实例,并将其添加进tDirectives数组中,并复制给match进行返回。
function addDirective(tDirectives, name, location, maxPriority, ignoreDirective, startAttrName, endAttrName) {
// 是被忽略的指令,返回null
if (name === ignoreDirective) return null;
var match = null;
// hasDirectives系统在初始化的时候添加的一个内健指令对象集合,$injector
if (hasDirectives.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
for (var directive, directives = $injector.get(name + Suffix),
i = 0, ii = directives.length; i < ii; i++) {
try {
directive = directives[i];
if ((maxPriority === undefined || maxPriority > directive.priority) &&
directive.restrict.indexOf(location) != -1) {
if (startAttrName) {
directive = inherit(directive, {$$start: startAttrName, $$end: endAttrName});
}
// 合法指令添加到tDirectives数组中
tDirectives.push(directive);
match = directive;
}
} catch (e) { $exceptionHandler(e); }
}
}
return match;
}
addAttrInterpolateDirective
addAttrInterpolateDirective处理当前节点中的属性。将其包装为一个指令供addDirectives调用。
- 首先利用
$interpolate处理html部分,并返回篡改函数。 - 在指令compile的pre过程中,将该属性的新旧变化放入监听函数中进行监听变化。
function addAttrInterpolateDirective(node, directives, value, name, allOrNothing) {
var trustedContext = getTrustedContext(node, name);
allOrNothing = ALL_OR_NOTHING_ATTRS[name] || allOrNothing;
// 处理html,返回篡改函数
var interpolateFn = $interpolate(value, true, trustedContext, allOrNothing);
// 没有需要监听处理的值 -> 忽略
if (!interpolateFn) return;
if (name === "multiple" && nodeName_(node) === "select") {
// 绑定到多个属性的节点时,报错
}
directives.push({
priority: 100,
compile: function() {
return {
pre: function attrInterpolatePreLinkFn(scope, element, attr) {
var $$observers = (attr.$$observers || (attr.$$observers = {}));
if (EVENT_HANDLER_ATTR_REGEXP.test(name)) {
// 不能篡改事件属性,报错
}
// 监听变化
var newValue = attr[name];
if (newValue !== value) {
interpolateFn = newValue && $interpolate(newValue, true, trustedContext, allOrNothing);
value = newValue;
}
if (!interpolateFn) return;
// 属性值初始化。例如{{name}} -> lwl
attr[name] = interpolateFn(scope);
($$observers[name] || ($$observers[name] = [])).$$inter = true;
(attr.$$observers && attr.$$observers[name].$$scope || scope).
$watch(interpolateFn, function interpolateFnWatchAction(newValue, oldValue) {
// 监听变化,设置属性值
if (name === 'class' && newValue != oldValue) {
attr.$updateClass(newValue, oldValue);
} else {
attr.$set(name, newValue);
}
});
}
};
}
});
}
addTextInterpolateDirective
若是文本节点,则同样创建内部指令,监听scope的变化然后设置节点的值。
function addTextInterpolateDirective(directives, text) {
var interpolateFn = $interpolate(text, true);
if (interpolateFn) {
directives.push({
priority: 0,
compile: function textInterpolateCompileFn(templateNode) {
var templateNodeParent = templateNode.parent(),
hasCompileParent = !!templateNodeParent.length;
if (hasCompileParent) compile.$$addBindingClass(templateNodeParent);
return function textInterpolateLinkFn(scope, node) {
var parent = node.parent();
if (!hasCompileParent) compile.$$addBindingClass(parent);
compile.$$addBindingInfo(parent, interpolateFn.expressions);
scope.$watch(interpolateFn, function interpolateFnWatchAction(value) {
node[0].nodeValue = value;
});
};
}
});
}
}
applyDirectivesTodNode
当收集了某个节点上的所有指令后,调用applyDirectivesTodNode方法将指令应用到当前的节点上,然后返回该指令生成的连接函数,即nodeLinkFn。applyDirectives方法遍历directives中的每一个指令,然后依次进行以下处理:
- 判断scope类型
- 判断是否需要有controller
- transclude的处理
- template的处理
- templateurl的处理
- compile处理
- terminal处理
有一点需要注意下,当当前的指令包括templateUrl时,即由需要异步处理的指令,先跳过,等到templateUrl部分进行集中处理。
当applyDirectivesToNode完成后,返回的nodeLinkFn函数如下,供链接过程中进行调用。
nodeLinkFn = {
scope = newScopeDirective && newScopeDirective.scope === true
transcludeOnThisElement = hasTranscludeDirective
elementTranscludeOnThisElement = hasElementTranscludeDirective
templateOnThisElement = hasTemplate
transclude = childTranscludeFn
}
directive.scope
如果directive声明了scope部分,若scope为对象时,则说明该指令需要独立作用域,利用newScopeDirective进行标记。源码如下:
if (directiveValue = directive.scope) {
// 跳过需要异步处理的指令,模板加载完成之后再处理
if (!directive.templateUrl) {
// scope属性为对象,例如{},则需要创建独立作用域
if (isObject(directiveValue)) {
newIsolateScopeDirective = directive;
}
}
newScopeDirective = newScopeDirective || directive;
}
directive.controller
如果directive声明了controller部分,则利用controllerDirectives存储当前节点上所有的controller,稍后进行赋值。源码如下:
// 同样,跳过要异步处理的指令,模板加载完成之后再处理
if (!directive.templateUrl && directive.controller) {
directiveValue = directive.controller;
// 收集当前节点上所用要创建的controller
controllerDirectives = controllerDirectives || createMap();
controllerDirectives[directiveName] = directive;
}
directive.transclude
transclude部分可以的取值有两种:element和true,这部分的处理也是分为了两种情况。
- element: 当设置为element时,要替换当前的节点,先用
$template暂存$compileNode,并将$compileNode给注释掉,然后编译$template并返回childTranscludeFn作为连接函数。 - true: 当设置为true时,只处理当前节点的子节点,
$template获取当前节点的内容,并编译$template并返回childTranscludeFn作为链接函数。
if (directiveValue = directive.transclude) {
hasTranscludeDirective = true;
// element
if (directiveValue == 'element') {
hasElementTranscludeDirective = true;
terminalPriority = directive.priority;
$template = $compileNode;
// 删除当前节点,替换为注释
$compileNode = templateAttrs.$$element =
jqLite(document.createComment(' ' + directiveName + ': ' + templateAttrs[directiveName] + ' '));
compileNode = $compileNode[0];
replaceWith(jqCollection, sliceArgs($template), compileNode);
// 编译当前节点
childTranscludeFn = compile($template, transcludeFn, terminalPriority, replaceDirective && replaceDirective.name, { nonTlbTranscludeDirective: nonTlbTranscludeDirective});
} else { // true
// 复制当前节点内容
$template = jqLite(jqLiteClone(compileNode)).contents();
// 清空当前节点
$compileNode.empty();
// 编译复制的内容
childTranscludeFn = compile($template, transcludeFn);
}
}
directive.template
template部分的处理比较繁琐,后面templateUrl部分的处理有些类似。
- 首先拿到directive.template,如果是函数的话,则函数返回值为模板内容,如果是字符串的话,则字符串本身为末班内容。
- 如果replace属性为true,说明使用模板来替换元素,被替换标签上的属性会被绑定到template的根元素上。用
replaceDirective暂存指令。- 用模板的第一个节点
compileNode替换当前节点$compileNode。 templateDirectives收集第一个节点compileNode上的所有指令。unprocessedDirectives暂存当前节点$compileNode剩余未编译的指令。- 将
$compile和compile的指令合并。 - 将
$compile和compile的属性合并。此时用template上的节点替换了原来的节点。
- 用模板的第一个节点
- 如果replace为false,直接将末班内容插入当前的节点
$compileNode上。
if (directive.template) {
hasTemplate = true;
templateDirective = directive;
// 如果template为函数,则函数返回值为模板内容
// 否则就是字符串,那么字符串就是模板内容
directiveValue = (isFunction(directive.template))
? directive.template($compileNode, templateAttrs)
: directive.template;
directiveValue = denormalizeTemplate(directiveValue);
// 如果replace为true
if (directive.replace) {
replaceDirective = directive;
if (jqLiteIsTextNode(directiveValue)) {
$template = [];
} else {
$template = removeComments(wrapTemplate(directive.templateNamespace, trim(directiveValue)));
}
// 模板的第一个节点
compileNode = $template[0];
if ($template.length != 1 || compileNode.nodeType !== NODE_TYPE_ELEMENT) {
// 没有要编译的内容或不是有效节点,报错
}
// 1.模板的第一个节点(compileNode)替换当前节点($compileNode)
replaceWith(jqCollection, $compileNode, compileNode);
var newTemplateAttrs = {$attr: {}};
// 2.收集模板的第一个节点(compileNode)的所有指令
var templateDirectives = collectDirectives(compileNode, [], newTemplateAttrs);
// 3.当前节点($compileNode)剩余未编译的指令
var unprocessedDirectives = directives.splice(i + 1, directives.length - (i + 1));
if (newIsolateScopeDirective) {
markDirectivesAsIsolate(templateDirectives);
}
// 4.$compileNode与compileNode的指令合并
directives = directives.concat(templateDirectives).concat(unprocessedDirectives);
// 5.将$compileNode与compileNode的属性合并
mergeTemplateAttributes(templateAttrs, newTemplateAttrs);
ii = directives.length;
} else {
// replace为false,直接将模板内容插入当前节点即可
$compileNode.html(directiveValue);
}
}
directive.templateUrl
和template类似,获取当前的模板,利用compileTemplateUrl进行编译,在参数中传入之前暂存的controllerDirectives等变量,在compileTemplateUrl中利用$http.get异步请求去调用相关文件,并类似template的方式进行节点的处理,返回链接函数。
if (directive.templateUrl) {
hasTemplate = true;
templateDirective = directive;
if (directive.replace) {
replaceDirective = directive;
}
// 和template的处理类似,只是在获取到模板之前,这些节点编译挂起
// 等获取到模板内容之后再继续编译
nodeLinkFn = compileTemplateUrl(directives.splice(i, directives.length - i), $compileNode,
templateAttrs, jqCollection, hasTranscludeDirective && childTranscludeFn, preLinkFns, postLinkFns, {
controllerDirectives: controllerDirectives,
newIsolateScopeDirective: newIsolateScopeDirective,
templateDirective: templateDirective,
nonTlbTranscludeDirective: nonTlbTranscludeDirective
});
ii = directives.length;
}
directive.compile
- 如果指令中存在compile字段,则
directive.compile为该指令的编译函数。由linkFn暂存其返回值。 - 返回值有两种情况:
- 如果返回的是函数,则该函数即为
post-link函数,将pre设为空利用addLinkFns保存链接函数。 - 如果返回的是对象,则其包括
pre-link和post-link两部分,利用addLinkFns保存链接函数。
// 同样,跳过需要异步处理的指令
if (!directive.templateUrl && directive.compile) {
try {
// 使用指令的compile函数编译指令
linkFn = directive.compile($compileNode, templateAttrs, childTranscludeFn);
// 如果返回的是函数,则该函数为post-link函数
// 否则返回为对象,pre和post属性分别对应指令的pre-link和post-link函数
if (isFunction(linkFn)) {
addLinkFns(null, linkFn, attrStart, attrEnd);
} else if (linkFn) {
addLinkFns(linkFn.pre, linkFn.post, attrStart, attrEnd);
}
} catch (e) {
$exceptionHandler(e, startingTag($compileNode));
}
}
directive.terminal
如果存在该属性,优先级小雨当前指令的不会被编译。
if (directive.terminal) {
nodeLinkFn.terminal = true;
terminalPriority = Math.max(terminalPriority, directive.priority);
}
publicLinkFn(scope)
当编译完成后,便返回了publicLinkFn的链接函数。这个方法执行编译过程中暂存的所有链接函数,创建scope并添加监听函数。
- 预处理(获取节点,绑定scope等)
- 若存在cloneConnectFn,则将
$linkNode和scope进行绑定。 - 若存在
compileNodes的返回值compositeLinkFn,则调用compositeLinkFn操作linkFns。由编译过程可知,此时linkFns包括该节点的链接函数nodeLinkFn和其子节点的链接函数childLinkFn。相当于循环的递归调用所有的nodeLinkFn。
function publicLinkFn(scope, cloneConnectFn, options) {
// 略去一大推
if (cloneConnectFn) cloneConnectFn($linkNode, scope);
if (compositeLinkFn) compositeLinkFn(scope, $linkNode, $linkNode, parentBoundTranscludeFn);
return $linkNode;
};
compositeLinkFn
循环遍历linkFns数组,取出链接函数。
- 创建子作用域。
- 若存在transclude,则利用
createBoundTranscludeFn创建childBoundTranscludeFn。 - 处理nodeLinkFn过程。
- 循环处理childLinkFn部分。
源码如下:
for (i = 0, ii = linkFns.length; i < ii;) {
node = stableNodeList[linkFns[i++]];
nodeLinkFn = linkFns[i++];
childLinkFn = linkFns[i++];
if (nodeLinkFn) {
if (nodeLinkFn.scope) {
// 新建子作用域
childScope = scope.$new();
} else {
// 使用父级作用域
childScope = scope;
}
// 包装一下TranscludeFn
if (nodeLinkFn.transcludeOnThisElement) {
// transclude: element
childBoundTranscludeFn = createBoundTranscludeFn(
scope, nodeLinkFn.transclude, parentBoundTranscludeFn,
nodeLinkFn.elementTranscludeOnThisElement);
} else if (!nodeLinkFn.templateOnThisElement && parentBoundTranscludeFn) {
childBoundTranscludeFn = parentBoundTranscludeFn;
} else if (!parentBoundTranscludeFn && transcludeFn) {
// transclude: true
childBoundTranscludeFn = createBoundTranscludeFn(scope, transcludeFn);
} else {
// 没有transclude属性
childBoundTranscludeFn = null;
}
// 实际链接处理就是nodeLinkFn了
nodeLinkFn(childLinkFn, childScope, node, $rootElement, childBoundTranscludeFn, nodeLinkFn);
} else if (childLinkFn) {
childLinkFn(scope, node.childNodes, undefined, parentBoundTranscludeFn)
}
}
createBoundTranscludeFn
如果存在transclude属性,则会调用createBoundTranscludeFn方法,主要是创建一个transcludeScope作用域,并调用之前编译$template获得的连接函数与新生成的transcludeScope进行绑定。
function (scope, transcludeFn, previousBoundTranscludeFn, elementTransclusion) {
createBoundTranscludeFn
var boundTranscludeFn = function(transcludedScope, cloneFn, controllers, futureParentElement, containingScope) {
if (!transcludedScope) {
transcludedScope = scope.$new(false, containingScope);
transcludedScope.$$transcluded = true;
}
return transcludeFn(transcludedScope, cloneFn, {
parentBoundTranscludeFn: previousBoundTranscludeFn,
transcludeControllers: controllers,
futureParentElement: futureParentElement
});
};
return boundTranscludeFn;
}
nodeLinkFn
nodeLinkFn函数非常重要。当一个指令使用独立作用域时,nodeLinkFn有以下操作:
- 根据指令的scope属性来构建独立作用域。
- 如果有控制器属性时,此时会调用控制器并初始化。
- 执行
prelinkfns和postlinkfns数组中的链接函数。
前两步代码如下:
// 1.创建独立scope
if (newIsolateScopeDirective) {
isolateScope = scope.$new(true);
}
// 2.创建控制器
if (controllerDirectives) {
elementControllers = setupControllers($element, attrs, transcludeFn, controllerDirectives, isolateScope, scope);
for (i in elementControllers) {
controller = elementControllers[i];
var controllerResult = controller();
// 略
}
}
在链接函数的执行过程中,分为三个步骤: preLinkFns->childLinkFn->postLinkFns。
- 其中,
preLinkFn执行顺序和文档节点顺序相同,因此可以将一些链接函数之前需要的预加载放在pre里执行。 - 递归执行所有子节点的链接函数。
postLinkFn是在递归回溯的过程中进行执行,和文档节点的顺序相反。
源码如下:
// 1.pre-link
for (i = 0, ii = preLinkFns.length; i < ii; i++) {
linkFn = preLinkFns[i];
invokeLinkFn(linkFn,
linkFn.isolateScope ? isolateScope : scope,
$element,
attrs,
linkFn.require && getControllers(linkFn.directiveName, linkFn.require, $element, elementControllers),
transcludeFn
);
}
// 2.递归执行子节点的链接函数
var scopeToChild = scope;
if (newIsolateScopeDirective && (newIsolateScopeDirective.template || newIsolateScopeDirective.templateUrl === null)) {
scopeToChild = isolateScope;
}
childLinkFn && childLinkFn(scopeToChild, linkNode.childNodes, undefined, boundTranscludeFn);
// 3.post-link
for (i = postLinkFns.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
linkFn = postLinkFns[i];
invokeLinkFn(linkFn,
linkFn.isolateScope ? isolateScope : scope,
$element,
attrs,
linkFn.require && getControllers(linkFn.directiveName, linkFn.require, $element, elementControllers),
transcludeFn
);
}
invokeLinkFn方法的主要功能如下:
linkFn(scope, $element, attrs, controllers, transcludeFn);
setupControllers
在nodeLinkFn方法中,利用setupControllers进行获取节点上的控制器。遍历传入的controllerDirectives参数,开始注册各个指令的控制器。
directive暂存取出含有controller的指令。- 生成包含
scope和element属性的对象locals。 - 调用
$controller生成控制器的实例controllerInstance,该实例是一个工厂函数,在外边进行调用执行。 - 将实例存入
elementControllers并进行返回。
源码:
function setupControllers($element, attrs, transcludeFn, controllerDirectives, isolateScope, scope) {
var elementControllers = createMap();
for (var controllerKey in controllerDirectives) {
var directive = controllerDirectives[controllerKey];
var locals = {
$scope: directive === newIsolateScopeDirective || directive.$$isolateScope ? isolateScope : scope,
$element: $element,
$attrs: attrs,
$transclude: transcludeFn
};
var controller = directive.controller;
// 特殊处理ng-controller
if (controller == '@') {
controller = attrs[directive.name];
}
// 生成控制器实例,实际是返回已经注入依赖的工厂函数
var controllerInstance = $controller(controller, locals, true, directive.controllerAs);
// 含有 transclude 指令的元素是注释
// jQuery不支持在注释节点设置data
// 因此,暂时将controller设置在local hash中
// 当 transclude 完成后,生成真正的节点之后,再将controller设置到data中
elementControllers[directive.name] = controllerInstance;
if (!hasElementTranscludeDirective) {
$element.data('$' + directive.name + 'Controller', controllerInstance.instance);
}
}
return elementControllers;
}